Enhancing Comfort and Reducing Costs
Energy Efficiency at Crystal
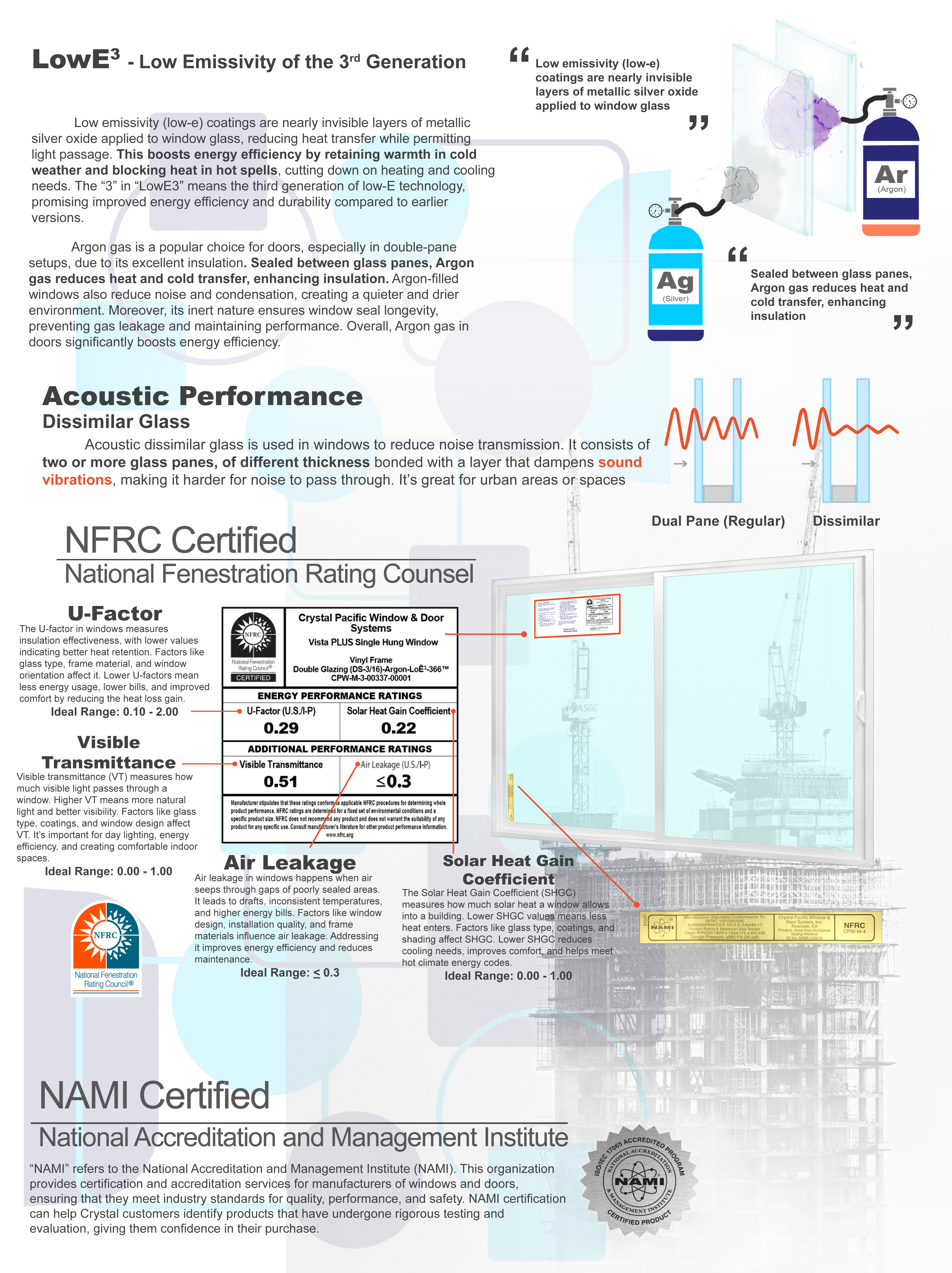
Energy-efficient windows and doors are designed to optimize indoor comfort while lowering energy consumption. By combining advanced technologies such as Low-E glass, insulated frames, and multi-pane designs with airtight seals, these products minimize heat transfer and reduce reliance on heating and cooling systems. Whether for residential or commercial applications, energy-efficient solutions not only cut utility costs but also contribute to a more sustainable future by reducing carbon footprints.
1. Frame Materials
- Vinyl Frames: Excellent insulators that reduce thermal bridging and energy loss.
- Composite Frames: Combine the strength of materials like fiberglass or aluminum with insulating cores.
- Wood Frames: Naturally insulating but require proper sealing and maintenance.
- Aluminum Frames with Thermal Breaks: Feature insulating barriers to prevent heat conduction through the metal.
2. Glazing Technology
- Low-E (Low Emissivity) Glass: Coated with a microscopic layer of metallic oxide to reflect infrared heat while allowing visible light to pass through.
- Double or Triple Glazing: Multiple panes of glass with insulating gas (argon or krypton) between them reduce heat transfer and improve thermal performance.
- Tinted Glass: Reduces solar heat gain and glare in sunny climates.
- Spectrally Selective Coatings: Block specific wavelengths of light to balance heating and cooling needs.
3. Gas Fills
- Argon or Krypton Gas: Used between panes of multi-glazed windows to improve insulation by slowing the transfer of heat.
4. Spacer Systems
- Warm-Edge Spacers: Separate glass panes in insulated glass units (IGUs) and reduce heat loss at the edges.
- Foam or Non-metallic Spacers: Provide better thermal performance compared to traditional aluminum spacers.
5. Weatherstripping and Seals
- High-quality weatherstripping and airtight seals prevent air leakage around windows and doors, enhancing energy efficiency.
6. U-Factor and Solar Heat Gain Coefficient (SHGC)
- U-Factor: Measures how well a window or door prevents heat from escaping; lower values indicate better insulation.
- SHGC: Measures how much solar heat enters a building through the glass; the ideal value depends on the climate.
7. Energy-Efficient Design
- Thermal Breaks: Layers of insulating material within the frame to reduce heat transfer.
- Operable Features: Windows like tilt-and-turn or hopper designs can improve ventilation while maintaining energy efficiency.
8. Certifications and Ratings
- ENERGY STAR® Certification: Indicates products meet specific energy performance criteria set by the U.S. Environmental Protection Agency.
- NFRC Ratings: Provide standardized metrics for U-Factor, SHGC, visible transmittance (VT), and air leakage.
How is Energy Efficiency Accomplished at Crystal Pacific?
Energy efficiency in windows and doors is achieved through a combination of design, materials, and technologies that work to reduce heat transfer, minimize energy consumption, and enhance indoor comfort. Check out how it’s applied in the list below the infographic.
By combining these elements, energy-efficient windows and doors help maintain indoor temperatures, lower heating and cooling costs, reduce environmental impact, and improve overall building performance. Let me know if you’d like more details on any of these aspects!







Let’s open doors together.
When you join us as a dealer, you’re not just gaining access to a wide selection of premium windows and doors; you’re joining a community that prioritizes excellence and innovation at every turn.
Fill out your information below, and we’ll get back to you shortly.
